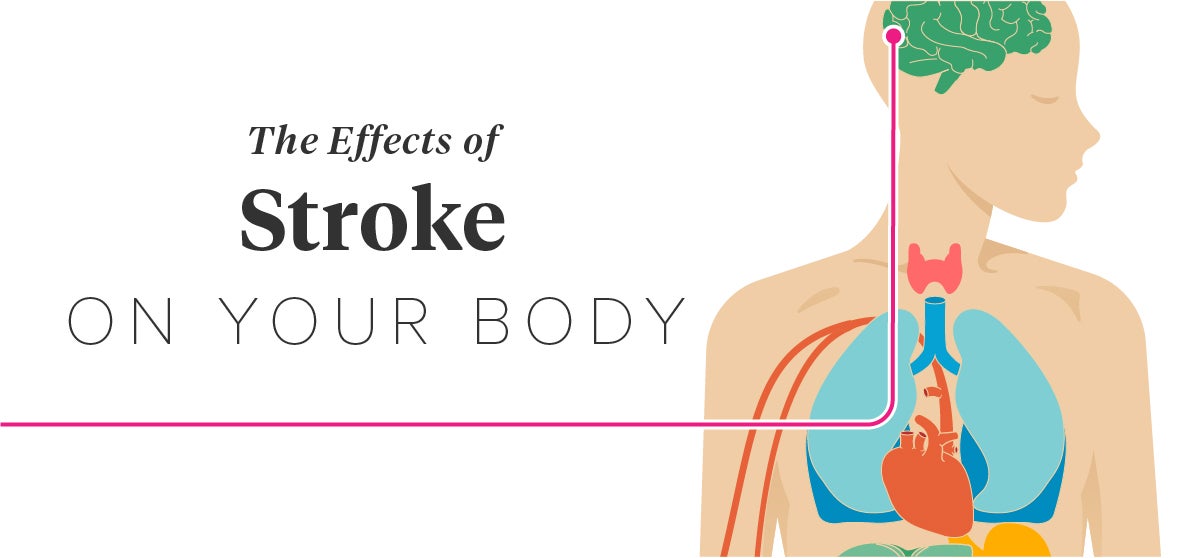
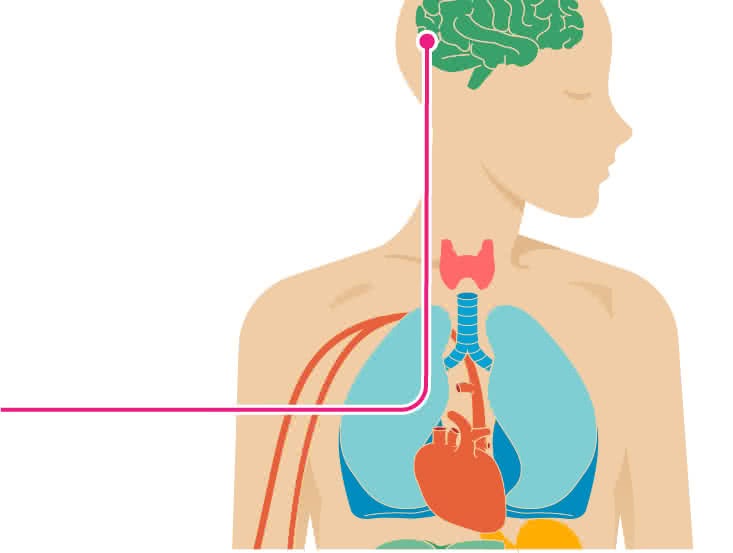
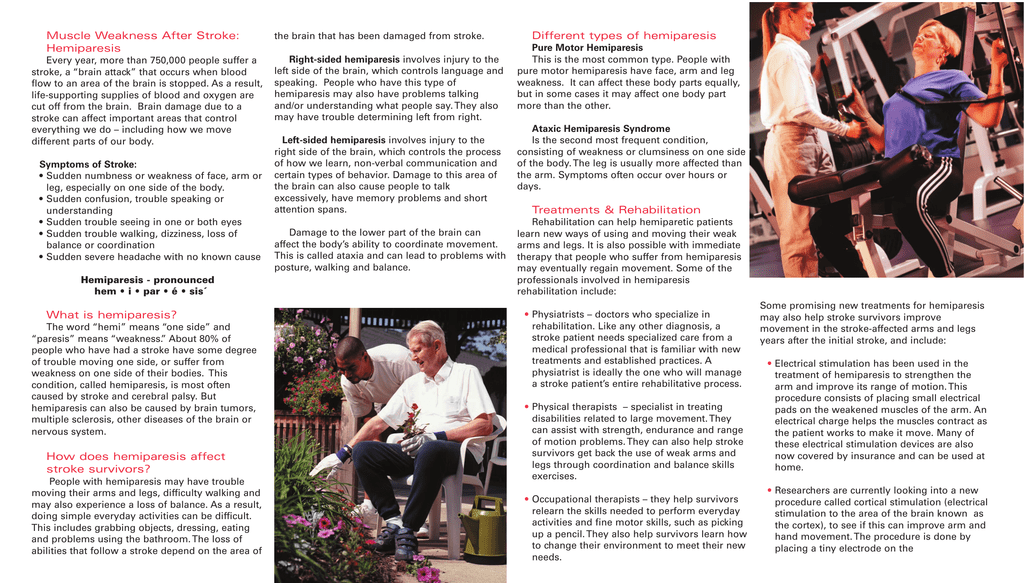
How Does A Stroke Affect The Musculoskeletal System
How does a stroke affect the musculoskeletal system. Unexplored areas in stroke rehabilitation and have poten-tially great clinical relevance. Stroke can cause muscle weakness or stiffness down one side of the body. In 2010 stroke cost about 737 billion in both direct and indirect costs in the US.
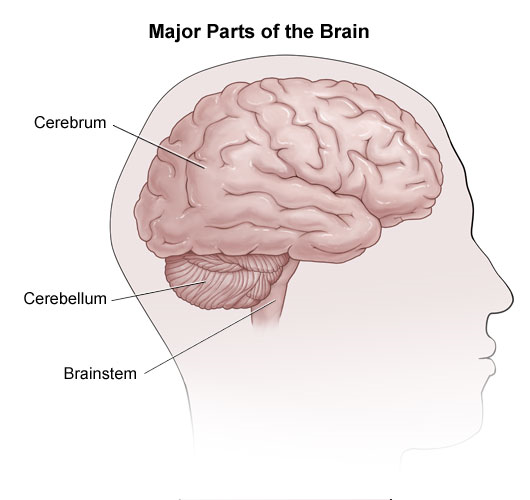
Find out more about this and the other physical effects of stroke. Feeling unaware of your position and movement in your limbs. It typically occurs when a stroke damages the part of the brain that sends inhibitory signals to the muscles.
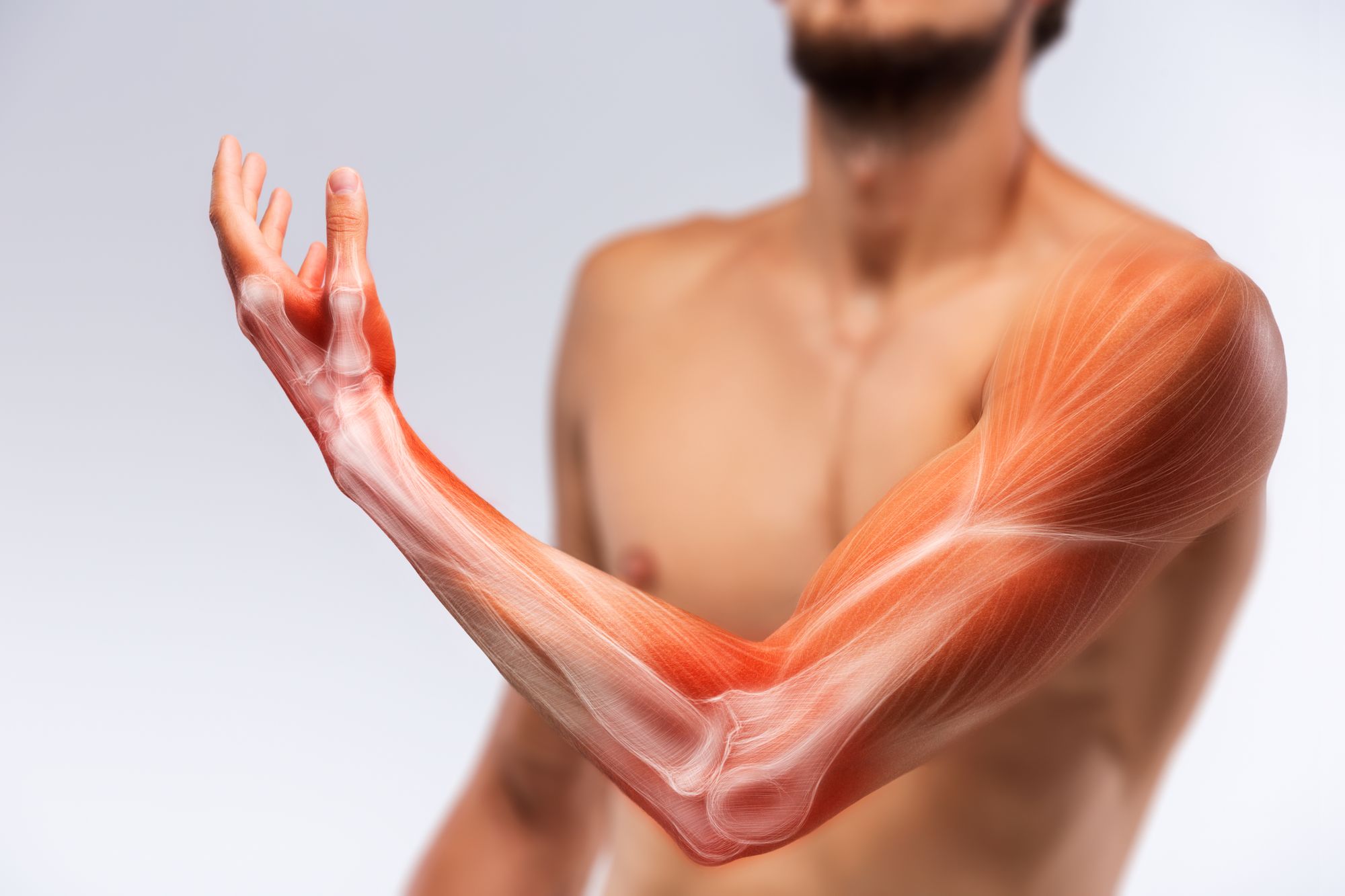
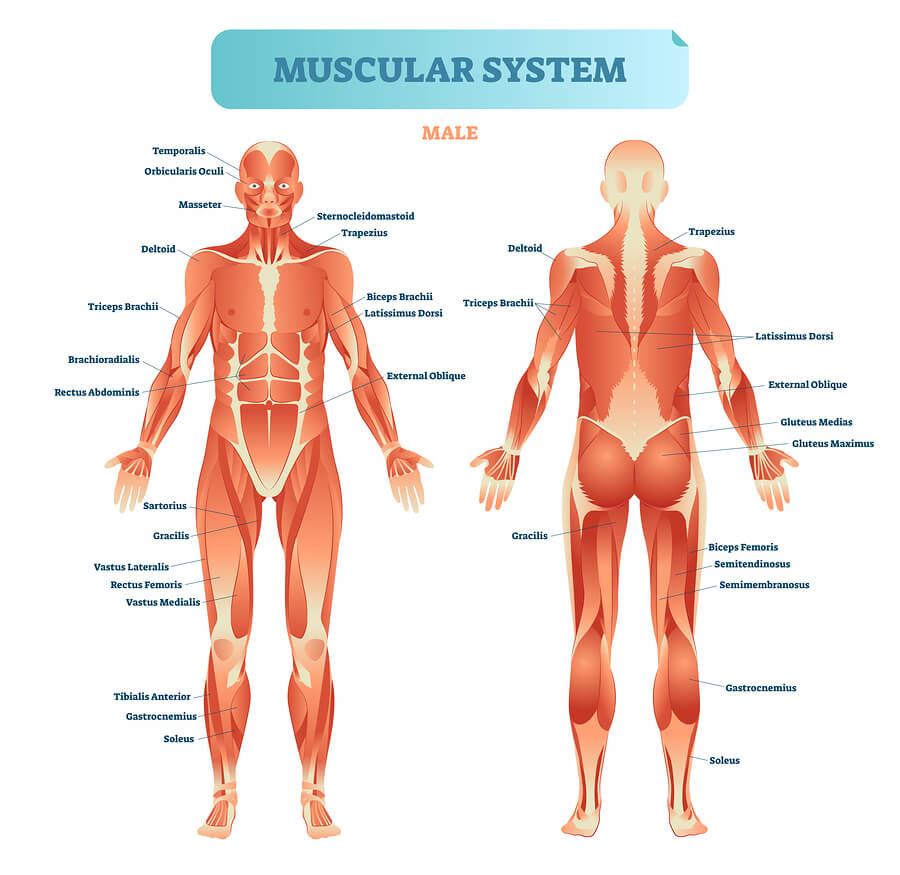
The musculoskeletal system is supported by the skeletal system. Hyperesthesia and can affect a range of your senses such as your taste hearing or touch. 32 Stroke-induced muscle fiber reductions lead to a decrease in muscle cross-sectional area.
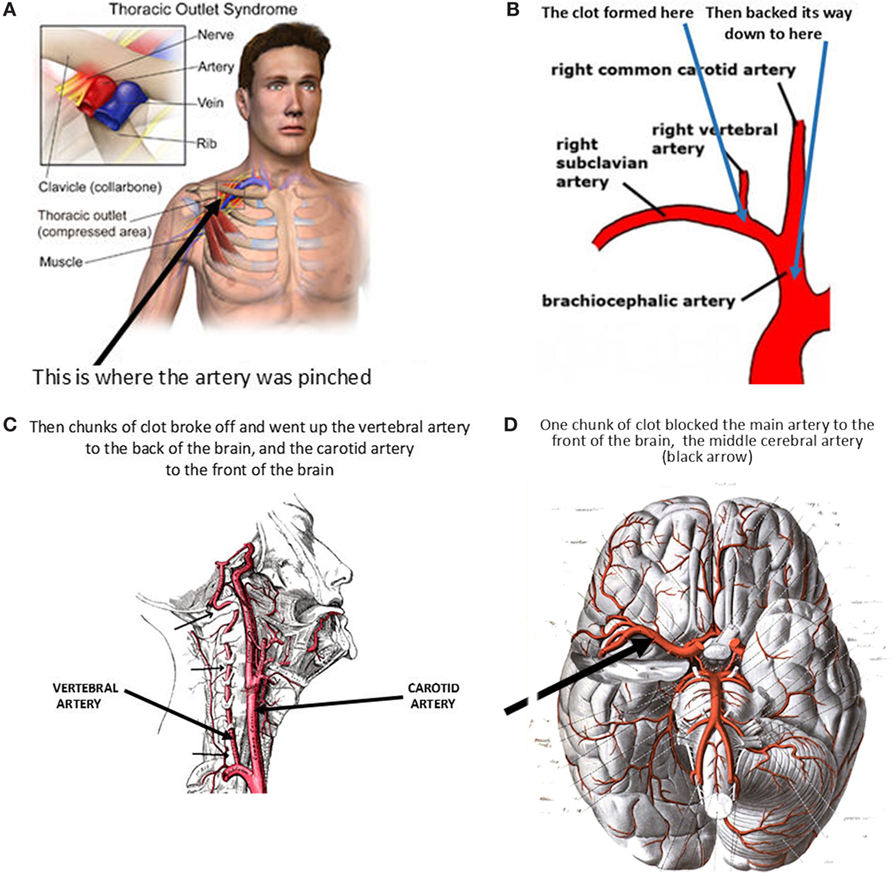
A stroke results in a lack of blood supply causing surrounding nerve cells to be cut off from their supply of nutrients and oxygen. The skeletal system also helps form your bodys shape. Persons with motor deficiencies following stroke are unable to direct nervous impulses to muscles in the different combinations used by persons with an intact central nervous system CNS.
When tissue is cut off from its supply of oxygen for more than three to four minutes it begins to die. These biological processes that occur in muscle with aging and inactivity are essentially unexplored areas in stroke rehabilitation and have potentially great clinical relevance. Loss of muscle sarcopenia is a process that starts around age 30 and progresses throughout life.
Following stroke patients may have swallowing impairment and other changes of the GI tract that could affect nutritional and hydration status and that lead to aspiration pneumonia. Strokes can appear as hemorrhagic strokes ischemic strokes or transient ischemic attacks. Stroke is a leading cause of serious long-term disability with an estimated 54 million stroke survivors currently alive today.
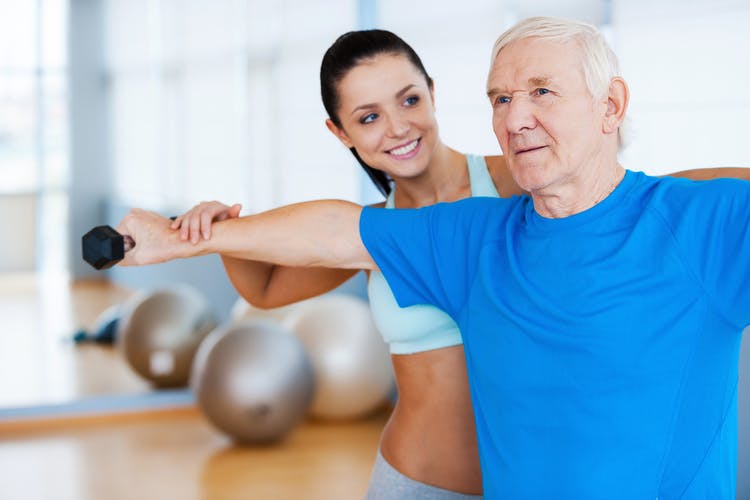
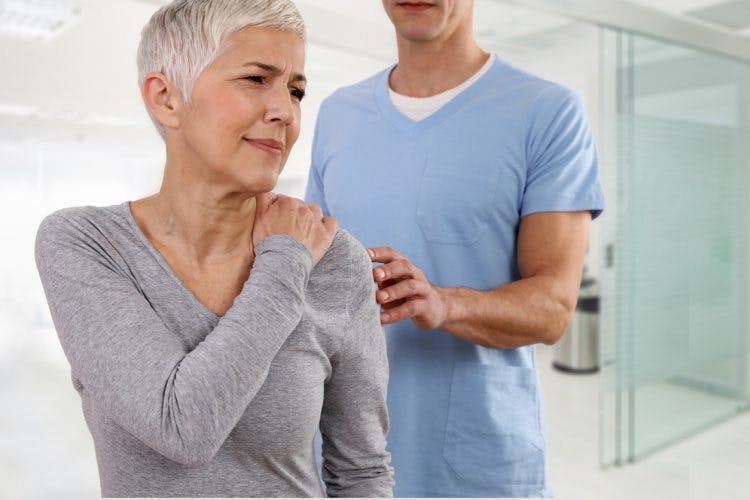
That means that near the bone you have fractured you will have a. Skeletal muscle following stroke may be affected by the altered central neural activation and spasticity similar to the muscle changes that occur after SCI.
Hypertonia refers to a high amount of muscle tone and increased tension in the muscles.
However in about 15 to 20 the stroke is progressive causing greatest loss of function after a day or two. In normal muscle functioning these signals instruct the muscles to relax when necessary. Furthermore those disruptions follow specific patterns depending on the severity of the stroke and the amount of time that has passed since the stroke. Stroke is a leading cause of serious long-term disability with an estimated 54 million stroke survivors currently alive today. Hyperesthesia and can affect a range of your senses such as your taste hearing or touch. The nature of these disorders dep. In this process the amount of muscle tissue and the number and size of muscle fibers gradually decrease. Unexplored areas in stroke rehabilitation and have poten-tially great clinical relevance. Skeletal muscle following stroke may be affected by the altered central neural activation and spasticity similar to the muscle changes that occur after SCI.
Find out more about this and the other physical effects of stroke. In eccentric hypertrophy the internal cavity dimension of the left ventricle is increased and this allows the heart to pump a greater volume of blood per beat stroke volume. The effects of a left hemisphere stroke may include. In normal muscle functioning these signals instruct the muscles to relax when necessary. Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States. The nature of these disorders dep. A stroke can cause paralysis difficulty swallowing or talking memory loss pain emotional changes and behavior issues.






/GettyImages-157434763-589e3a935f9b58819c047635.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-effects-of-a-frontal-lobe-stroke-3146431-v2-7746fa1f13e84345be19dcb0402156b3.jpg)
















/stroke-symptoms-4014442-ADD-FINAL-363bb8055b8a4d56bc7752fc217d06c2.jpg)







Post a Comment for "How Does A Stroke Affect The Musculoskeletal System"